Depression is a condition that can prevent a person from leading a normal life. While temporary sadness is normal, persistent sadness can overwhelm a person that can affect the health, relations and social life.
A number of factors could explain why patients with depression have a higher risk of heart disease. A study by researchers at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) found that people with coronary heart disease who have been diagnosed with depression are about twice as likely to die than those who have not been diagnosed with depression.
The National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) focus on patients with coronary heart disease that causes reduced blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body, causing heart attack, strokes, heart failure, and death. Although coronary heart disease is the most common form of heart disease, killing more than 1.5 million people in the United States each year, it also comes under the umbrella of other leading causes of death, including cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and stroke.
Research suggests that depression can be a factor in the development and progression of cardiovascular disease, as well as heart attack and stroke.
Some Facts About Depression

- Depression is a mental health disorder in which people experience depressed mood and loss of interest in the activities that cause a noticeable impairment in the life of the individual.
- Depression is also called Major Depressive Disorder or Clinical Depression.
- There can be a combination of causes for this condition including biological, psychological and social factors.
- Depressed people are more prone to develop increased platelet reactivity, increase in proinflammatory markers, and a decrease in heart variability.
- A study revealed that depression after recovery from a major heart condition increased the risk of mortality to 17% within the period of 6 months after a heart attack episode.
- Negative lifestyle habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with the treatment of depression as well as the heart disease.
Signs of Depression
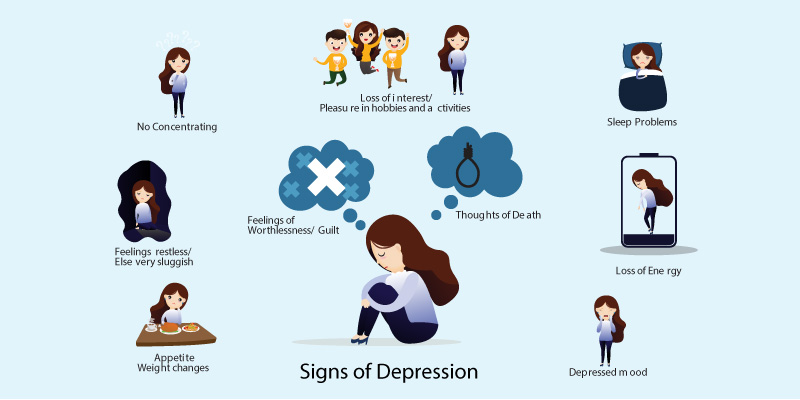
According to American Psychiatric Association, depression symptoms can range from mild to severe. Some symptoms may include,
- Persistent feeling of sadness or low mood
- Loss of interest in the previous pleasurable activities
- Changes in diet or appetite- overeating or lack of appetite
- Increased fatigue
- Feelings of worthlessness and hopelessness
- Problems with concentration and thinking
- Suicidal thoughts
It should be noted that these symptoms must last for at least two weeks to be diagnosed with depression.
Risk Factors of Depression
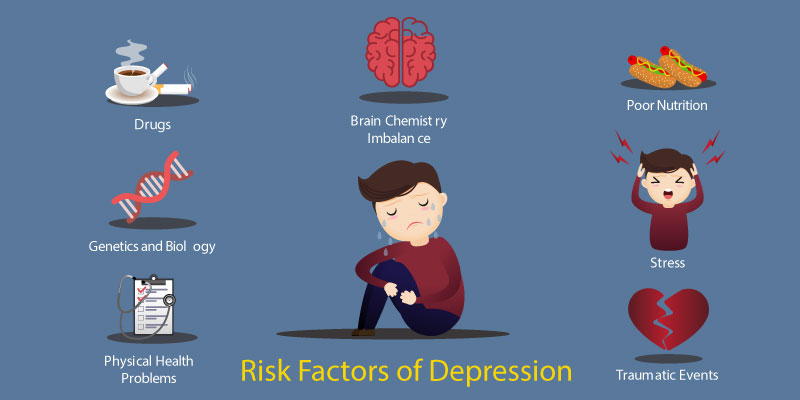
There are several factors that can develop the risk of depression in a individual:
- Genetics: If someone has a family history of depression, the chances of depression increases.
- Environmental Factors: If an individual has been in continuous exposure to abuse, violence, and emotional neglect, chances of depression increases.
- Biochemistry: Changes in the brain chemical can lead to depression.
- Personality: If an individual has low self-esteem, chances of suffering from depression increases.
It is to be noted that not above mentioned risk factors are not the only reasons for someone to develop depression. Any individual can suffer from depression. However, people who associate with the aforementioned factors are at higher risk of developing depression.
Depression and Heart Problems
While researchers are still investigating how depression can trigger heart problems, they have identified several mechanisms as possible culprits. People with depression typically have a decreased heart rate variability, which can be caused by changes in blood flow to the heart, such as a drop in blood pressure or loss of oxygen in the blood.
Depression and heart problems are highly likely to be linked in a number of ways. Moreover, depression in people with existing heart-related conditions can make the recovery more difficult. People with depression are more prone to indulge in unhealthy lifestyle behaviour such as excessive alcohol consumption, regular smoking, overeating or eating less, constant stress, and ignoring medication. Due to these reasons, such individuals develop the risk of heart problems, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
However, Depression is the cause of heart problems, it can develop in a reversible manner too. While diagnosing heart disease or a heart attack can increase the risk of depression, depression itself can also increase the likelihood of developing heart disease. In patients with acute heart attacks, the symptoms of depression are similar to those of the general population, strongly indicating a link between depression and heart disease.
Conclusion
Depression is the condition which can cause an individual to experience a halt in their daily activities. It is generally characterized by feelings of loss of interest, increased fatigue, lowered mood, negative cognitions, loss or appetite, and suicidal thoughts at worst.
It is well known that depression is highly likely to be experienced by an individual who has suffered with some kind of heart disease. Alternatively, depression can increase the risk of developing a heart disease in a healthy person. During the depression phase, stress hormones are released in increased amounts which not only affect the cardiac rhythm but also put a major pressure on the blood vessels which can cause several other diseases such as hypertension.
Dealing with depression alone may put an overwhelming pressure on the mind and body. Hence, it is always recommended to consult the doctors at regular intervals of time to make sure that recovery of the mind and the heart is not hindered in any way.