Heart Failure is a serious condition where the heart is unable to supply a sufficient amount of blood to the body. When the body doesn’t get sufficient blood supply, the major functions get disturbed.
There are many conditions including narrowed arteries, blocked arteries, or high blood pressure that can make the heart weak or stiff and further result in Heart Failure.
Some Facts About Heart Failure
- Heart Failure is also interchangeably termed as Congestive Heart Failure, where the heart muscles are not able to pump the blood properly.
- It is concluded that Heart Failure is the collection of conditions or symptoms that stiffen or weaken the heart to pump blood efficiently.
- According to the report of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 6.5 million Americans have Heart Failure.
- In the report, men are more affected than women but the mortality rate of women is considerably higher than men if the condition goes untreated.
- In some cases of Heart Failure, the heart has a difficulty to supply blood to the organs or body for proper functioning. However, in other cases, the stiffening or hardening of the heart muscles reduce or block the blood flow.
- Heart Failure can affect the right side of the heart, the left side of the heart, or both sides of the heart at the same time.
- Heart Failure can be acute where the symptoms appear suddenly and disappear quickly. It is also known as a heart attack.
- Heart Failure can also be chronic where symptoms are continuous and ongoing. These symptoms are improved over time. It is interesting to know that most of the Heart Failures are chronic.
Types of Heart Failures
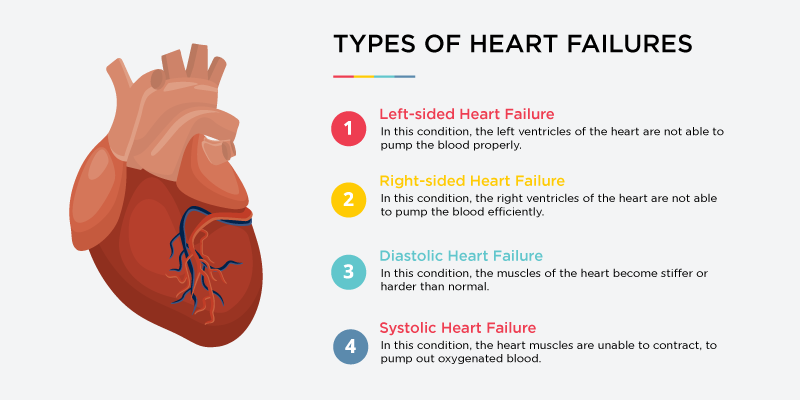
As discussed earlier, Heart Failure can affect either the right side or the left side of the heart. It can affect both sides of the heart as well. So, here are some of the types of Heart Failure:
Left-sided Heart Failure
This type of Heart Failure is very common and most Heart Failure cases are recorded as left-sided Heart Failure. In this condition, the left ventricles of the heart, which pump the oxygenated blood to the body are not able to function properly. This reduces the supply of oxygenated blood to the body. And, when the organs are able to get the oxygenated blood, the blood goes back into the lungs for oxygen. This results in shortness of breath and fluid build-up.
Right-sided Heart Failure
In this type of condition, the right ventricles of the heart which pump the blood to the lungs for the collection of oxygen are not able to function efficiently. This condition is usually triggered due to left-sided Heart Failure. The left ventricle failure makes it difficult for the right ventricle to work properly and cause the heart to fail. It can also be a result of some lung diseases.
Diastolic Heart Failure
In this type of Heart Failure, the muscles of the heart become stiffer or harder than normal. This stiffness usually occurs due to heart disease and makes it difficult for the heart to fill with blood. This problem is also called Diastolic Dysfunction, which causes less supply of blood to the rest of the body.
Systolic Heart Failure
In this condition, the heart muscles are unable to contract, which is important to pump out oxygenated blood to the body. The problem is also called Systolic Dysfunction, which occurs due to a weak heart.
Causes of Heart Failure
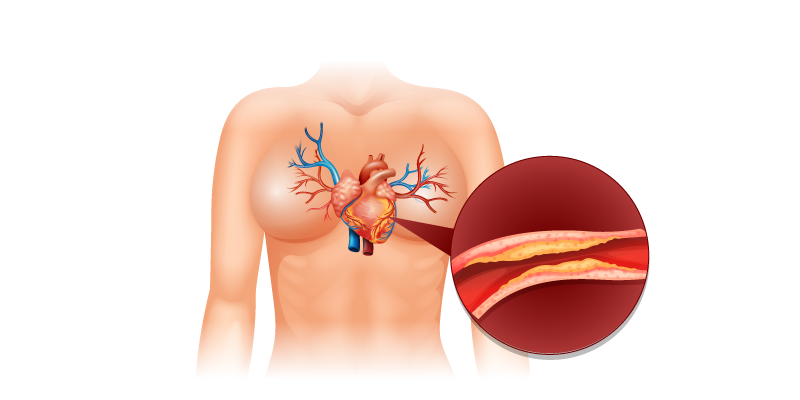
Heart Failure usually occurs after other heart conditions have weakened the heart. The most common among them is Coronary Artery Disease (CAD). However, it can also occur when the heart becomes too hard.
In some Heart Failure cases, the ventricles, the ones responsible for pumping blood, lose their ability and become stiff. In other cases, the weak heart muscles create stress on the ventricles to that point that they are not able to pump the blood efficiently. And over time, the heart is not able to perform its functions properly.
Other than that, there are many heart conditions that increase the chances of Heart Failure. Some of the risk factors include:
- Cardiomyopathy where the heart becomes weak
- Heart attack
- Congenital heart defect
- Heart valve disease
- Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats)
- Myocarditis, inflammation of the heart
- High blood pressure
- Emphysema (lung disease)
- Hypothyroid or Hyperthyroid
- Diabetes
- Severe Anemia
- HIV
- AIDS
- Some Cancer treatments like Chemotherapy
- Drugs or Alcohol substances
Symptoms of Heart Failure
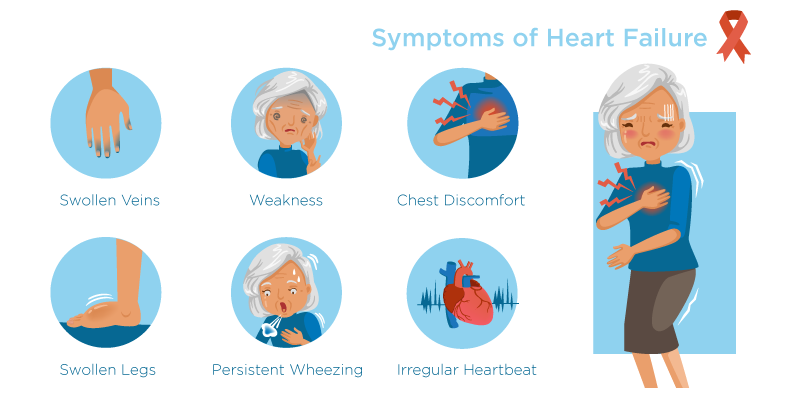
Some of the common symptoms associated with Heart Failure are:
- Excessive weakness or fatigue
- Sudden weight gain
- Frequent urination
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Persistent wheezing or coughing
- Irregular heartbeat or pulse
- Heart palpitations
- Abdominal swelling
- Difficulty in breathing
- Ankle and leg swelling
- Difficulty in concentration
- Swollen neck veins
- Chest pain, if it is caused by a heart attack
Diagnosis of Heart Failure
To diagnose this condition, doctors will review the patient’s medical history carefully, examine the symptoms, and perform the physical examination. Doctors or the medical team will also check for risk factors such as Coronary Artery Disease, Diabetes, Blood Pressure, etc. They also check the lungs for congestion and legs and ankles for fluid build-up.
First using a stethoscope, they check the pulses and heartbeat. After that, the best way to diagnose Heart Failure is by Echocardiogram which uses sound waves to create a clear image of heart so that the doctors can evaluate any damage to the heart. This also helps in determining the associate cause of the condition. Along with this, doctors also perform many tests, which include:
- Blood tests
- Chest X-ray
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Stress test
- Cardiac computerized tomography (CT) scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Coronary angiogram
- Myocardial biopsy
Conclusion
Heart Failure is a serious health condition which requires early treatment to improve the signs and symptoms and lower the chances of complication. Along with treatments, some lifestyle changes and dietary changes can also help in improving the condition and managing the symptoms. However, one should always consult expert Cardiologists or professional doctors before opting for any treatment or lifestyle changes.