Heart Attack occurs when the build-up of fat, cholesterol, and other substances block the flow to the heart. The build-up usually forms a plaque in the arteries that help in circulating the blood to the heart or from the heart. Any blockage in this way causes hindrance in the normal blood circulation and when the heart doesn’t get a sufficient amount of blood to pumped up, the reflex reaction of the heart can be termed as Heart Attack.
Some Common Facts about Heart Attack
- It is estimated that every year, about a million Americans have Heart Attack.
- Heart Attack is also known as Myocardial Infarctions (MI), where “Myo” refers to muscle, “Cardial” refers to the heart, and “Infraction” means the death of tissue due to insufficient or lack of blood supply.
- Because of the insufficient supply of blood and the death of tissue during Heart Attack, the muscles of the heart get damaged.
- The chances of Heart Attack increase for women above 55 and men above 45.
- This problem can be fatal. However, there are treatments available for this. Always call or seek professional help in case of any emergency or noticeable symptoms.
Causes of Heart Attack
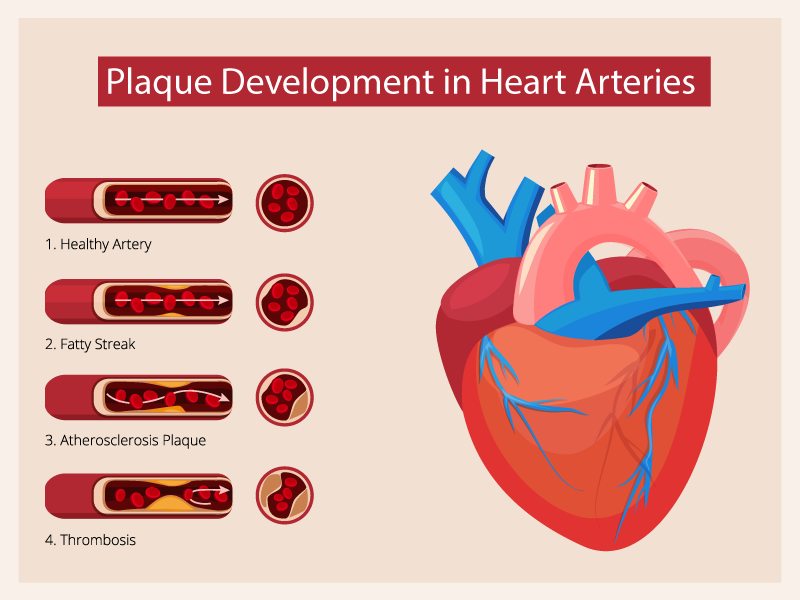
There are many causes and risk factors associated with Heart Attack. Here are some of the most common causes of a Heart Attack:
- It generally happens when one or more coronary arteries are blocked due to the buildup of excess fat or cholesterol.
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) in which the coronary artery gets narrowed due to some plaque can also cause Heart Attack. This is one of the most common causes of Heart Attack.
- Arrhythmias in which the heart beats either too slow or fast can also cause Heart Attack
- Another cause can be Cardiogenic Shock when the blood pressure suddenly drops and the heart is not able to circulate enough blood to the body.
- Hypoxemia can also be a cause of Heart Attack. In this condition, the oxygen level in the blood becomes very low and the heart is not able to supply oxygenated blood to the body.
- Sometimes the fluid accumulates in and around the lungs (Pulmonary Edema) can also hinder the normal functioning of the heart and cause Heart Attack
- Sometimes the blots clot in the deep vein of legs or pelvis. This condition is known as Deep Vein Thrombosis and interrupts the normal blood flow in the vein. This can further lead to a Heart Attack.
- Myocardial Rupture can also cause Heart Attack as in this condition the walls of the heart get damaged or rupture and interrupt the normal heart functioning.
- Some lifestyle habits can also cause Heart Attacks such as consuming tobacco and illicit drugs. These harmful substances can cause a sudden involuntary contraction of the artery and shut down the flow of blood to the heart and from the heart.
- Eating high-fat content foods can also increase the change of Heart Attack
Symptoms of Heart Attack

Though there are many symptoms of Heart Attack, the below symptoms are listed by the American Heart Association (AHA):
- Discomfort, tightness, pressure, heaviness, squeezing, or pain in the chest, back, arm, or below the breastbone
- Discomfort that goes into the neck, throat, or jaw
- Shortness of breath
Other Heart Attack signs and symptoms include:
- Fast, slow, irregular heartbeat
- Severe weakness, fatigue, anxiety, dizziness
- Indigestion, fullness, heartburn, or choking feeling
- Vomiting, nausea, upset stomach, abdominal pain
- Coughing, chest pain, restlessness
The symptoms can vary from person to person. However, it is always recommended to consult a professional doctor in case you notice any of the symptoms.
How to Diagnose Heart Attack

The Diagnosis of Heart Attack will be done by doctors after performing the physical examination and reviewing the patient’s medical history. There are several tests available that help in diagnosing Heart Attack. These tests include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): ECG or EKG is a test performed to monitor the electrical activity of heart (heart rate and rhythm). It helps to know how much heart muscle has been ruptured or damaged. It is a simple and noninvasive procedure.
- Blood Test: Blood test is very common in all diagnosis processes and it is also performed in the diagnosis of Heart Attack or heart diseases. The different cardiac enzymes in the blood can indicate the damage of heart muscles. Usually, there are many enzymes present inside the heart cells. In case these cells are damaged, ruptured, or injured, the heart cell content including these cardiac enzymes spill into the bloodstream. Doctors perform the blood test to measure the levels of these cardiac enzymes in the blood. This will help the doctors to figure out when the Heart Attack started and the size of the Heart Attack. Also, when the heart muscles get damaged due to insufficient blood supply, the proteins inside the heart are also released. The blood tests also measure the levels of proteins in the heart, i.e. troponins.
- Echocardiography: It is another diagnosis method for Heart Attack. Echocardiography is an imaging test that is performed to know how the heart is pumping and what are the areas that aren’t pumping. The “echo” will tell whether any parts (septum, valve, etc.) of the heart are damaged or not.
- Cardiac Catheterization: Doctors may perform Cardiac Catheterization during the first hours of Heart Attack in case the patient is not responding to the medications. It will give a clear view of blocked artery so that doctors can decide the best treatment for the patient.
These are the common processes that help to diagnose the Heart Attack and decide the optimal treatment for the patient.
Conclusion
Heart attack is a death of heart muscles due to less blood supply. Heart Attack is one of the serious issues that can be treated by doctors. The best way to deal with Heart Attack is by consulting doctors in case of any noticeable symptoms for a long time.