Coronary Artery Disease occurs when the blood vessels or arteries that supply oxygen, blood, and nutrients to the heart become impaired or damaged. In this condition, the plaque (cholesterol, fat, or other substances) deposits in the arteries, causing a lack of blood supply to the heart. When this plaque develops, the coronary arteries become inflamed and the way to flow the blood to the heart becomes narrowed.
Some Interesting Facts About Coronary Artery Disease
- Coronary Artery Disease is also known as Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) or Atherosclerotic Heart Disease (AHD), which is caused due to plaque buildup in the coronary arteries.
- Due to this plaque build-up, the inner walls of coronary arteries become stiff and narrow, causing lower blood flow, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
- The blockage may take decades to develop and a complete blockage can lead to a Heart Attack or Sudden Cardiac Arrest.
- Because the blockage takes many years to buildup, you may not notice any significant symptoms or signs of Coronary Artery Disease.
- There are four primary coronary arteries on the surface of the heart where the build can develop: the right main coronary artery, left main coronary artery, left circumflex artery, and left anterior descending artery.
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is one of the most common heart diseases resulting in 365,914 deaths in 2017 and about 18.2 million adults over 20 have Coronary Artery Disease, according to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
Causes of Coronary Artery Disease
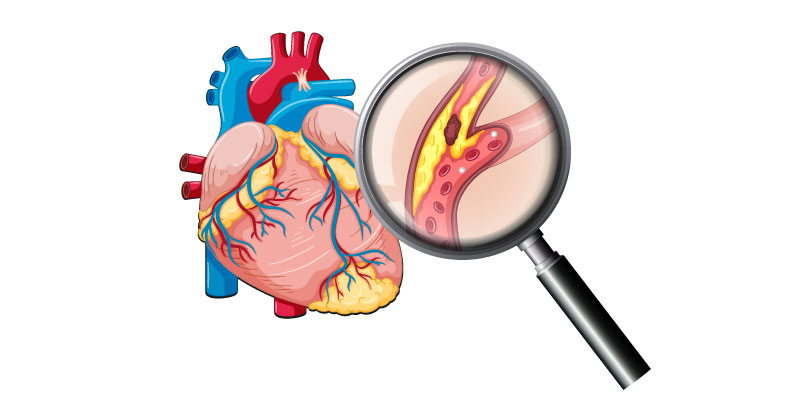
Atherosclerosis (vascular injury with plaque buildup) is the most common cause of Coronary Artery Disease. The coronary artery is a network of blood vessels that help in supplying the blood to the heart. When these arteries get damaged due to plaque deposits or other factors, it may lead to coronary arteries disease.
Apart from plaque development, the various risk factors of Coronary Artery Disease include:
- Age: As people grow older, the risk of impaired and narrowed coronary arteries increases.
- Gender: According to the CDC report, men are more prone to Coronary Artery Disease than women. However, the risk increases in women after menopause.
- Family History: People with a family history of heart disease are at greater risk of having Coronary Artery Disease.
- Smoking: Smoking is one of the three most common risks of heart disease and secondhand smokers are at higher risk of developing Coronary Artery Disease.
- High Blood Pressure: Another common risk factor is High Blood Pressure. It can thicken and stiffen the arteries so that the blood cannot flow efficiently.
- High Cholesterol: High levels of blood cholesterol can increase the risk of plaque development (atherosclerosis). It is also one of the leading causes of heart disease and Coronary Artery Disease. Generally, high cholesterol can be caused due to low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or bad cholesterol. However, good cholesterol or high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol can also cause the formation of plaque.
- Diabetes: Diabetes is also associated with Coronary Artery Disease because people with CAD and Diabetes have similar risk factors such as High Blood Pressure and obesity.
- Obesity: Obesity also increases the chance of getting Coronary Artery Disease. It can also worsen the condition.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of physical activity can increase the chance of Coronary Artery Disease and its risk factors like obesity.
- Stress: Stress can trigger many diseases and one such disease is coronary heart disease. It can also increase the chance of other risk factors as well.
- Unhealthy Diet: Eating too much food that is rich in saturated and trans fats, sugar, and salt can also increase the chances of getting Coronary Artery Disease.
CDC report says that among the above risk factors, High Blood Pressure, High Cholesterol, and smoking are the most common reasons for heart disease. And, approximately half of the Americans have at least one of three risk factors i.e., High Blood Pressure, High Cholesterol, or smoking.
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease

Coronary Artery Disease occurs due to excessive buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries. There can be no visible early symptoms of this condition as it slowly develops. However, there are some of the visible symptoms, including:
- Chest pain (angina)
- Tightness or pressure in the chest
- Physical stress
- Shortness of breath
- Numbness
- Squeezing
- Pain in the shoulders and arms
- Pain in the neck and jaw
- Sweating
- Dizziness
- Weakness
- indigestion
- heartburn
- Cramping
Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease
To diagnose this condition, doctors first review the physical examination, medical history, and medical tests. Some of the common tests to diagnose CAD include:
- Electrocardiogram: The electrical signals of the heart can be monitored with the help of an Electrocardiogram. This helps doctors to know whether the person has had a Heart Attack.
- Echocardiogram: It is an imaging test that shows the clear image of the heart and helps to determine whether the heart is working properly or not.
- Heart CT Scan: In this test, doctors check for any plaque deposition in the arteries of the heart.
- Cardiac Catheterization: In this procedure, doctors inject dye in the coronary arteries with the help of the catheter. This helps in identifying the blockage or plaque.
- Stress Test: This test reveals or measures the stress level of the heart while resting or during physical activity. It helps in comparing the stress level while a person walks or at rest. In this test, nuclear imaging can also be done.
Conclusion
Coronary Artery Disease is a medical condition that can cause other serious problems such as Heart Attack or Sudden Cardiac Arrest. It is always advisable to consult a doctor in case of any noticeable symptoms.