Does high cholesterol cause heart disease or not? This is one of the popular concepts that researchers are studying for years in order to find the perfect evidence that shows link between cholesterol and heart disease. In this article, we will try to understand these studies and know whether the two are connected or not.
To start with, let’s know;
What is Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a fat-like, waxy substance present in the bloodstream. Cholesterol is made by the liver to insulate nerves and to build certain hormones and cells. Though Cholesterol is made by the liver, the food and diet also help in making cholesterol. Foods like eggs, milk, meat, etc., support the body to make cholesterol. Cholesterol helps in building new healthy cells, but an excess amount of it is harmful to heart health. High cholesterol and heart disease are always linked with each other. So, this article focusses on the evidence that answers the very popular question: does high cholesterol cause heart disease?
To begin with, first understand the types of Cholesterol:
- High-density Lipoprotein (HDL): It is also called good cholesterol. It eliminates cholesterol from the blood and returns it to the liver for ejection.
- Low-density Lipoprotein (LDL): Generally, it is called bad cholesterol. It helps in carrying the cholesterol to those body parts which are in need of it. Excess amount of LDL in the bloodstream can cause accumulation on the walls of arteries which results in blocking the arteries and reducing blood flow. This can increase the risk of heart attack, heart failure, and stroke.
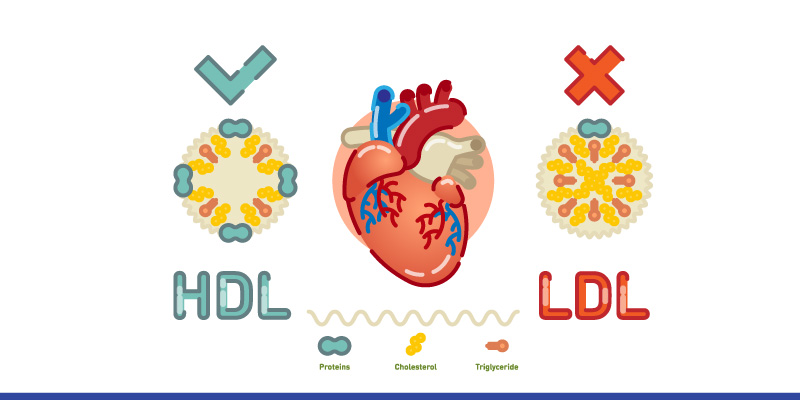
If the total cholesterol level is high due to excessive LDL in the bloodstream, there are higher chances of heart diseases or stroke. However, if the total cholesterol level is high only due to increased HDL, there is no such risk.
Another type of fat is Triglycerides that is present in the blood. When a person intakes more calories than the body requirement, it transforms the extra calories into triglycerides.
The ideal level of cholesterol and heart disease risk:
- Total cholesterol level: It should be less than 200. However, it always depends on the LDL and HDL levels.
- LDL cholesterol levels: The ideal LDL level should be less than 130. More than may increase the chances of heart disease.
- HDL cholesterol levels: Ideally, it should be 60 or higher to reduces the chances of heart disease.
- Triglycerides: It should be less than 150 mg/dl.
Up til now, we have discussed about cholesterol and heart disease risk. Lets explore some studies related to this.
Does High Cholesterol Cause Heart Disease? What Research Says
For decades, researches and studies have shown that diet and levels of cholesterol play a significant role in keeping the heart healthy. According to many recent studies, the connection between cholesterol and heart disease is complex. Let’s dig into more to know.
The Connection between High Cholesterol and Heart Disease

According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans of 2010, the consumption of dietary cholesterol should be limited to 300 mg a day. On the other hand, the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015-2020 doesn’t specify any limit but suggested consuming dietary cholesterol as minimum as possible. In this, there are many trials and studies mention that shows strong evidence of the association between Cholesterol and heart disease. It is concluded that eating healthy foods that contain low dietary cholesterol help reduce the occurrence of heart diseases in adults.
Another study published in 2016 shows that raised LDL levels can increase heart disease risk. This eight-week conducted study also states that dietary fatty acids play an important role in heart disease development.
Also, researchers found that changing dietary patterns (for example replacing some bad cholesterol-containing foods with good quality foods) reduced the risk of high cholesterol and eventually lower the heart disease risk.
Another side of this Research
Many newer researchers examine and question the role of high cholesterol in heart disease development.
A review published at BMJ Jornoul in 2016 found that older people (age above 60) with high levels of LDL live the same or longer life than people with low LDL. However, in justification, other researchers recommend reconsidering the prevention guidelines for heart disease in older adults.
The review has some constraints as it didn’t look at HDL levels, health conditions, cholesterol-lowering medications, and lifestyle factors.
Role of Trans Fats
Trans fats increase the level of LDL and decrease HDL levels. According to the American Heart Association, both LDL and HDL levels are connected with the chance of heart disease development. Also, Trans fats don’t offer any nutritional value.
The main source of these fats are Partially hydrogenated oils (PHOs) in daily diets. PHOs are present in variety of processed foods.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2018 recommended that the consumption of PHO is not safe for humans.
What we conclude
There should be more studies and researches to be conducted to find out does high cholesterol cause heart disease. However, there are many reliable studies present that show the impact of cholesterol on heart health. Also, it is a well-known fact that excess of anything can be harmful to health and this is also true in cases of cholesterol. Foods that are rich in cholesterol and trans fats should be consumed less as they increase the chances of obesity which further increases the risk of heart disease.
Causes High Cholesterol
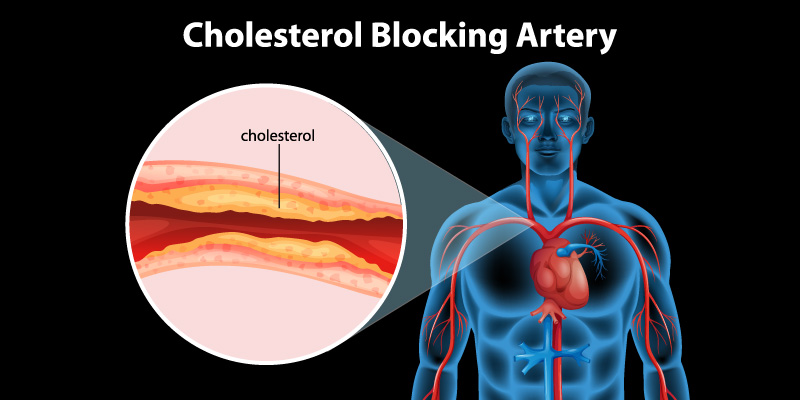
The liver makes cholesterol, but the body gets cholesterol from food as well. Consuming too many high-cholesterol foods can increase the level of cholesterol in the bloodstream. This is one of the main causes, other causes that can increase the cholesterol level include:
- Being overweight means that a person has a high level of triglycerides
- Being physically inactive can lower the level of good cholesterol (HDL)
- Family history of high cholesterol
- Smoking also decreases the level of HDL
Risk Factors include:
- Poor Diet
- Older age
- Gender
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Liver disease
- Hypothyroidism
- Kidney disease
Diagnosis of High cholesterol

To check the levels of cholesterol, doctors perform blood tests to determine the lipid panel or lipid profile. Generally, the report contains:
- Total cholesterol level
- LDL cholesterol level
- HDL cholesterol level
- Triglycerides level
For accurate measurements, don’t consume any food and liquid (other than water) for approximately 9 to 12 hours before the blood test.
Conclusion
High cholesterol can be harmful to heart health and overall health. This is why it is recommended to intake less quantity of high cholesterol foods. Also, visit your doctor and check for cholesterol levels once in a while.