Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is a broad term used for the conditions associated with the sudden lack of blood supply to the heart. The condition may occur due to the fat accumulation in and on the walls of the coronary artery. Another reason for this blood clots in the coronary arteries. The blockage may develop instantly, suddenly or over a period of time.
Coronary arteries are responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood and delivering nutrients to the heart. And, for the proper functioning, the heart needs oxygen-rich blood and nutrients. However, sometimes these coronary arteries are unable to work properly and disturb the heart functioning as well. In patients with coronary artery syndrome, the blood supply to the heart gets reduced than usual.
The types of Acute Coronary Syndrome are determined by the blockage location, amount of damage that occurs, and the length of time that the blood flow is blocked. Based on this, doctors classify ACS as:
- The presence of substance build-up or accumulation in the blood which can damage the heart functioning
- Symptoms
- The results of Electrocardiography (ECG)
ACS can also be described by using the following coronary artery disease:
- Unstable Angina: Unstable angina is a condition that occurs when the cells do not die, but heart muscles or tissues get damaged due to reduced supply of oxygen and further disturbs the heart to work properly or efficiently. This condition can be permanent or temporary. So, the condition when Acute Coronary Syndrome does not causes cell death is termed as unstable angina.
When the oxygen supply to the cells reduces, the chances of heart muscles cells death increase. This reduced blood supply to heart muscles or tissue is termed as ischemia which further leads to the damaged muscle tissue. This is known as a heart attack or myocardial infarction (MI).
- NSTEMI or Heart Attack: Non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction or NSTEMI is a type of heart attack which occurs when the coronary arteries get partially blocked
- STEMI or Heart Attack: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction or STEMI is also a type of heart attack which occurs when the coronary arteries get completely blocked.
Some Common Facts About Acute Coronary Syndrome
- Acute Coronary Syndrome is an umbrella term for medical conditions in which the blood supply to the heart is suddenly reduced.
- Heart attack and unstable angina are common types of coronary syndrome.
- According to Ann Bolger, a cardiologist, M.D., at San Francisco General Hospital and a member of the Council on Clinical Cardiology in the American Heart Association, ACS is an absolute medical emergency that can occur in a minute and disturbs the blood flow to the heart.
- According to the estimation of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, someone has a heart attack every 20 seconds in the U.S.
- This estimation also shows that approximately 805,000 Americans suffer from a heart attack every year, out of which 605,000 people are diagnosed with a heart attack for the first time.
- And, 200,000 people have a recurrent heart attack
- Nearly, 1 in 5 heart attacks is silent which means that the heart muscles get damaged, but the patient is not aware of it.
- The prompt diagnosis, treatment, and care help in improving the blood flow and preventing future complications and problems.
Causes of Coronary Acute Coronary Syndrome
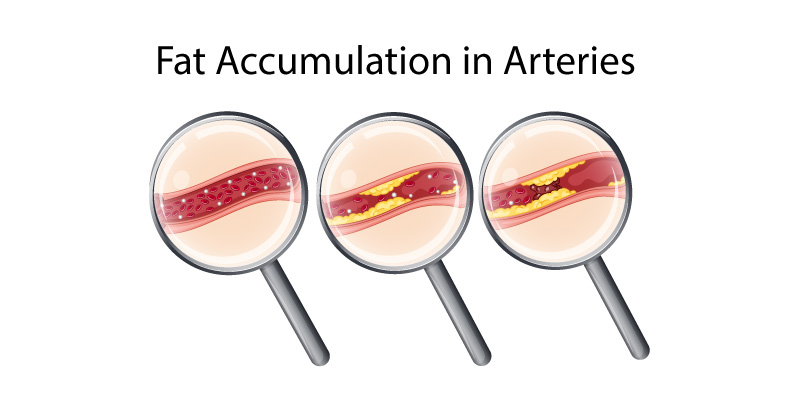
ACS is generally caused due to the fat build-up or accumulation in or on the coronary artery walls. The blood vessels help in supplying oxygen and nutrients to the heart. These deposits form blood clots and hinder the flow of blood to the heart. The lack of oxygen supply to muscle tissues can lead to cell death and damage of heart muscles. And, further increases the chances of heart attack or MI.
The plaque contains white blood cells, LDL, fats, bad cholesterol, and other substances.
Risk factors include:
- Age: men over 45 and women over 55.
- Smoking cigarette
- High blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Less physical activity
- Overweight
- Unhealthy diet
- Family history of heart disease or chest pain
- History of high blood pressure, diabetes, or preeclampsia
Symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome

The signs and symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome include:
- Chest pain (angina)
- Chest discomfort
- Tightness or pressure on the heart
- Chest muscle strain
- Heartburn
- Indigestion
- Vomiting or nausea
- Breathlessness
- Heavy sweating
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Fainting
- Unusual fatigue
- Feeling restless
- Pain spreading to arms, shoulders, back, upper abdomen, neck or jaw
Diagnosis of Acute Coronary Syndrome

In cases a person has symptoms related to Acute Coronary Syndrome, the doctors will take some initial tests, ask a question about symptoms and medical history, and also check for any underlying conditions. The initial diagnosing tests include:
- Blood Test: This test helps in identifying certain enzymes that present if the blood cells are impaired or dead. The positive result of this test indicates the chances of a heart attack.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This helps in identifying the electrical activity of the heart that may disturb due to lack of blood flow. The patterns may also help in determining the location of the blockage.
Based on the result of these tests and symptoms, doctors start a primary diagnosis of Acute Coronary Syndrome. Further tests include:
- Coronary Angiogram
- Echocardiogram
- Myocardial perfusion imaging
- Computerized tomography (CT) angiogram
- Stress test
Conclusion
Acute Coronary Syndrome is a collective term used for diseases related to sudden or decreased blood supply to the heart. The condition is serious and required medical attention as soon as a person notices any symptoms related to the disease.